What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that generates new content, rather than merely analyzing existing data. It can generate text, images, audio, video, and even code based on patterns it has learned from large datasets.
Unlike traditional AI, which is mostly used for predictions or classifications, generative AI models are designed to create something new. That’s where the word “generative” comes from. These systems learn how humans write, draw, speak, or compose music, and then use that knowledge to produce similar outputs.
Think of generative AI like an advanced assistant. You type a few words asking for a blog introduction, and it generates one for you. You upload a photo and request a new version in a painting style; it delivers it. Tools like ChatGPT, DALL·E, Midjourney, and Google’s Gemini are real-world examples of generative AI in action.
What is the Difference Between Traditional AI and Generative AI?
Traditional AI is designed to analyze data, identify patterns, and make decisions. It helps with tasks like fraud detection, spam filtering, and recommendation systems. In simple terms, it answers questions based on existing data.
Generative AI takes a different approach. It learns from large datasets and creates new content, such as text, images, or code. Tools like ChatGPT and DALL·E are examples, capable of writing articles or generating visuals from scratch.
While traditional AI is great for automation and prediction, generative AI is built for creativity and content generation. Businesses use both, depending on whether they want to streamline operations or create personalized, original experiences.
How Generative AI Works
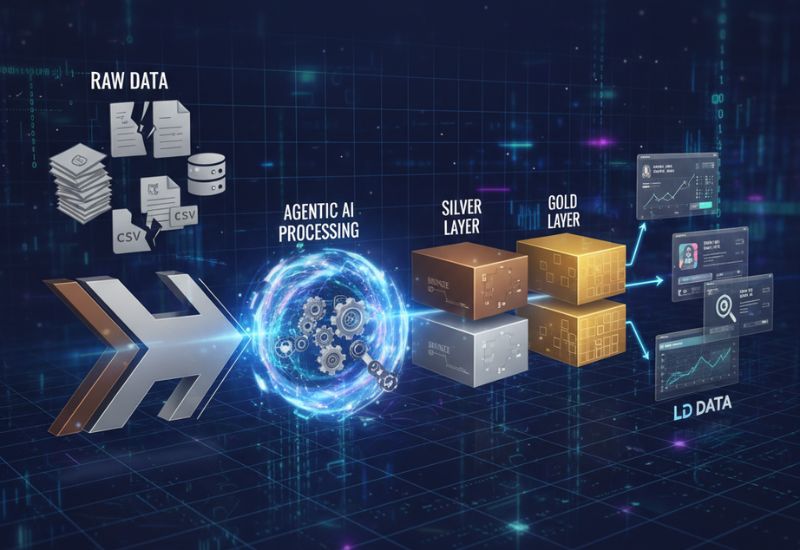
Generative AI works by learning patterns from large amounts of data and then using that knowledge to create new content. At the core of this process are machine learning models, especially deep learning architectures like transformers, which power tools such as ChatGPT and DALL·E.
During training, these models are fed massive datasets, like books, images, or audio, to understand how humans write, speak, or design. Over time, the AI learns relationships between words, shapes, or sounds, which is especially valuable in generative AI for data analytics, where pattern recognition leads to automated insights. it predicts what should come next based on what it has learned.
For example, if you ask a generative AI tool to write a blog introduction, it looks at the prompt, finds similar examples from its training, and generates a response that fits naturally. The same idea applies to image generation, music composition, or coding.
In simple terms, generative AI mimics human creativity using patterns and probabilities. It doesn’t understand content like a person does, but it can produce results that feel thoughtful and original.
Best Practices for Using Generative AI
Adopting generative AI can transform the way businesses operate—from automating tasks to generating content, designs, code, and more. But like any powerful technology, it needs to be used responsibly and effectively.
Here are some essential best practices for using generative AI in your organization.
1. Start with Clear Business Objectives
Before you choose a generative AI tool or model, ask:
- a. What problem are we trying to solve?
- b. Where can generative AI create real value?
For example, marketers may use generative AI tools to generate campaign ideas or content variations, while software teams might use AI coding assistants to speed up development.
Tip: Begin with low-risk use cases such as generating internal documents or social media drafts before scaling to customer-facing content.
2. Choose the Right Generative AI Technology
Not all generative AI models are built the same. Choose based on your needs:
- a. Text generation: GPT-4, Claude, Gemini
- b. Image generation: DALL·E, Midjourney
- c. Code generation: GitHub Copilot, Tabnine
- d. Business applications: Jasper, Copy.ai, Notion AI
Whether it’s for marketing, development, or operations, selecting the right generative AI services ensures scalability and impact from the start.
3. Maintain Human Oversight
AI can assist, but it shouldn't operate without human review.
- a. Always fact-check AI-generated content
- b. Monitor for brand consistency and tone
- c. Have humans in the loop for decision-making tasks
This protects against misinformation and ensures ethical AI use, especially in sensitive areas like healthcare or finance.
4. Ensure Data Privacy and Compliance
Generative AI tools often require access to data. It’s your responsibility to:
- a. Use anonymized or synthetic data where possible
- b. Check compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, or local regulations
- c. Review the privacy policy of third-party generative AI applications
Trustworthy use of AI builds long-term credibility with customers and stakeholders.
5. Train Your Teams
Successful adoption isn’t just about the tool, it’s about the people using it.
- a. Provide hands-on training for teams
- b. Encourage experimentation while setting boundaries
- c. Promote an AI-aware culture within your organization
Training helps unlock the full potential of generative AI for business while reducing misuse or confusion.
6. Define Ethical Boundaries
Be intentional about where and how you use AI. Set clear internal guidelines around:
- a. Acceptable use
- b. Intellectual property and plagiarism
- c. Bias detection and fairness
Many businesses now include AI ethics in their company policies to avoid reputational and legal risks.
By following these best practices for using generative AI, you not only maximize value but also build trust and responsibility into your AI strategy.
Generative AI Model Architectures and How They’ve Evolved
Generative AI has progressed rapidly thanks to evolving model architectures that power its capabilities. Here's a quick overview of how these models have developed:
1. Early Approaches
Initial generative AI models were rule-based and statistical, such as Markov chains and n-gram models. They were limited in flexibility and often produced repetitive results.
2. Neural Networks and RNNs
The introduction of neural networks, especially recurrent neural networks (RNNs), enabled the generation of sequential data like text and time series. However, RNNs struggled with long-term context.
3. GANs and VAEs
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) brought a major breakthrough, enabling realistic image and media generation. Around the same time, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) offered a probabilistic way to reconstruct and generate data, useful in tasks like image synthesis.
4. Transformers
Transformers changed the game by processing entire sequences at once using attention mechanisms. Models like GPT and BERT enabled more coherent text generation, forming the core of many modern generative AI applications.
5. Diffusion Models
Recently, diffusion models have gained popularity for high-quality image generation. They reverse a noise process to create detailed and diverse visuals and are widely used in tools like DALL·E and Stable Diffusion.
6. Hybrid Models
Today’s generative AI models often combine multiple architectures, like transformers with GANs to enable more advanced and multimodal outputs. These advancements are expanding generative AI use cases in business, design, and research.
What Are the Applications of Generative AI?
Generative AI is quickly becoming a valuable asset across industries. From content creation to scientific research, its applications are diverse, practical, and growing every day. Let’s explore the most impactful areas where generative AI technologies are making a difference.
1. Language and Text Creation
Text-based generation is the most advanced and widely adopted form of generative AI. Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT are being used to write articles, generate summaries, translate content, and even assist with code development. Businesses rely on these tools to streamline communication, create marketing content, and automate routine writing tasks.
2. Audio and Music Generation
Generative AI is also making progress in audio. With simple text prompts, AI models can create songs, sound effects, and voiceovers. These tools are being used in podcasts, games, and videos, making audio production faster and more accessible—even without professional equipment or studios.
3. Visual Content and Design
In the visual space, generative AI helps create logos, edit images, design 3D models, and generate illustrations. Marketers and designers are using it to produce visuals for social media, websites, ads, and virtual experiences. These models also allow businesses to experiment with different styles and creative concepts quickly.
4. Synthetic Data Generation
One of the most impactful generative AI applications is creating synthetic data. When real data is limited, private, or hard to access, AI can generate realistic datasets for training other machine learning models. This is especially useful in fields like autonomous driving, where virtual road scenarios improve testing, and in healthcare, where privacy restrictions limit data sharing. Generative AI is also redefining how businesses approach analytics, especially in making sense of complex or limited datasets through AI-driven data insights.
5. Healthcare and Life Sciences
Generative AI supports healthcare professionals by automating tasks like medical report writing, image analysis, and genomic data interpretation. It also plays a major role in medical research, helping scientists discover new drug compounds and protein structures, speeding up the drug development process and improving diagnostics.
6. Automotive and Transportation
In the automotive sector, AI is used to design 3D components and simulate real-world driving scenarios. These simulations are helping to safely test autonomous vehicles and speed up the car development process. It reduces risk, cuts costs, and enhances vehicle safety through more controlled testing environments.
7. Climate and Scientific Research
Generative models are being used to simulate weather patterns, predict natural disasters, and model environmental changes. These applications help researchers and policymakers better prepare for climate risks and improve early warning systems for natural events like floods or storms.
6. Entertainment, Gaming, and Media
The entertainment world is one of the most exciting spaces for generative AI use cases. From scriptwriting and animation to game design and world building, creators are using AI to speed up production while exploring new creative possibilities. Rather than replacing human creativity, AI acts as a powerful support tool that brings ideas to life faster.
From generating text to simulating real-world environments, the applications of generative AI are wide-ranging and evolving fast. These tools are not just about automation, they’re about enhancing human creativity, improving productivity, and solving real-world problems like data analysis with generative AI.
Benefits of Generative AI
Generative AI is becoming a key part of modern business. It helps teams save time, lower costs, and stay creative. Whether you run a startup or a large company, the benefits are hard to ignore.
1. Faster Content Creation
Generative AI can quickly create content like text, images, videos, and music. What used to take hours can now be done in minutes. This helps teams meet deadlines without lowering quality.
2. Improved Productivity
AI tools handle time-consuming tasks such as writing emails, analyzing data with generative AI, or suggesting code.This gives teams more time to focus on planning, problem-solving, and creative work.
3. Better Personalization
AI makes it easier to create content that feels personal. From custom emails to tailored visuals, it helps connect with your audience in a more meaningful way, which can improve engagement and results.
4. Cost Savings
Hiring teams to create large amounts of content can be expensive. Generative AI reduces this cost by doing much of the work automatically. This is especially helpful for small businesses with limited budgets.
5. Supports Innovation
With AI, teams can test ideas faster and explore new directions. Whether it’s designing a product or running simulations, AI allows for more experiments without needing a lot of time or money.
6. Easy to Use
You don’t need to be a tech expert to use generative AI. Marketers, teachers, founders, and designers can all use it to build content, websites, or lessons. This makes advanced tools available to more people.
7. Scales With You
As your business grows, AI helps you keep up. It can create content, write code, or support customers at a much larger scale without needing to grow your team as fast.
The benefits of generative AI go far beyond automation. It helps businesses work faster, explore new ideas, and stay ahead.
Challenges, Limitations, and Risks of Generative AI
Generative AI is a powerful tool, but it is not perfect. Like any new technology, it comes with risks and limitations that businesses should be aware of before using it widely.
1. Accuracy and Misinformation
Generative AI can create content that sounds right but may be factually wrong. Since it works by predicting what comes next based on patterns, it does not always check for accuracy. This can be risky in areas like health, law, or business communication.
2. Bias in Results
AI models learn from data found online or in documents, which can sometimes include unfair or biased information. This means the output may reflect those same biases. It's important to check the content before using it publicly.
3. Privacy Concerns
If the AI has been trained on personal or private data, it may accidentally include sensitive information in its results. To stay safe, businesses should make sure they are following data privacy laws and protecting user information.
4. Legal and Ethical Issues
There are still questions around who owns AI-generated content. Sometimes the AI may copy parts of existing work without meaning to. There is also the risk of using AI to create fake content, which can damage trust if misused.
5. High Costs and Technical Needs
Some generative AI tools need a lot of computer power to work well. This can be expensive or hard to manage, especially for smaller teams or companies with limited resources.
The risks and limitations of generative AI do not mean you should avoid it. They mean you should use it with care. With human review, clear guidelines, and the right tools, AI can be helpful and safe.
Conclusion
Generative AI is changing the game, creating new content like text, images, and music. It helps businesses churn out content faster, personalize experiences, and innovate, all while saving costs.
But it's not without its quirks. We need to be mindful of accuracy, potential biases, and privacy issues. With smart planning, the right tools like trusted generative AI services, and human oversight, generative AI can be a powerful ally, boosting our creativity and tackling real-world challenges.