What is Data Governance?
Data governance is a framework that defines how data is managed, accessed, and used across an organization. It ensures that data is accurate, secure, consistent, and used responsibly.
For example, in a retail company, data governance helps maintain consistent customer information across regions, avoiding duplication or reporting errors. A clear data governance model sets rules for data entry, access, and quality.
In data analytics, data governance ensures that teams work with reliable data, leading to better insights and decisions. It's not just about control, it's about trust and value in every piece of data used.
What Does Data Governance Do?
Data governance establishes the rules, roles, and responsibilities for managing data within an organization. It defines who can access data, how it's classified, stored, and protected, and ensures data stays accurate and consistent across systems.
It also supports compliance with regulations, improves data quality, and reduces risks related to poor data handling. Data governance helps businesses make better decisions, keep their data safe, and trust their insights.
Why Data Governance Matters
In today’s data-driven world, organizations rely heavily on data to make strategic decisions, drive innovation, and stay competitive. However, without proper controls, data can quickly become fragmented, duplicated, outdated, or even misused. This is where data governance really helps.
Data governance provides a structured approach to managing data, ensuring it is accurate, consistent, secure, and accessible to the right people. It helps organizations set clear policies and standards around data usage, storage, privacy, and compliance.
For example, in regulated industries like finance or healthcare, poor data handling can lead to legal issues or data breaches. Enterprise data governance helps minimize these risks by enforcing compliance and accountability across the organization.
It also improves data quality, reduces operational inefficiencies, and enhances the value of data for analytics and reporting. With a solid data governance strategy, businesses can make confident decisions, improve customer trust, and unlock the full potential of their data assets.
In short, data governance matters because it transforms raw data into a reliable foundation for growth, compliance, and innovation.
Data Governance vs. Data Management
Data governance and data management aren’t the same, though they support each other.
Data governance is the strategic framework. It sets the rules and roles that help keep data correct, safe, and used the right way. It answers the "who," "what," and "why" of who can access the data, what rules apply, and why the data matters.
On the other hand, data management focuses on the operational side, how data is stored, organized, integrated, and maintained on a day-to-day basis. It includes processes like data warehousing, moving data between systems, and backing it up.
Key Elements of Data Governance
A successful data governance strategy is built on several core elements that ensure data is well-managed, high-quality, and aligned with business goals. Here are the key components:
1. Data Policies and Standards
These rules explain how to gather, store, use, and access data. Well-defined data governance policies help maintain consistency and ensure compliance across departments.
2. Data Stewardship
Data stewards are responsible for enforcing governance policies and ensuring the accuracy and quality of data. They help connect business teams with IT.
3. Data Ownership and Accountability
Every dataset should have a clearly defined owner responsible for its integrity and security. This creates accountability and supports stronger enterprise data governance.
4. Data Quality Management
Poor data leads to poor decisions. One of the key goals of data governance is to monitor and improve data quality through validation rules, error detection, and cleansing processes.
5. Metadata Management
This involves organizing and maintaining data about data, such as where it came from, how it’s formatted, and who modified it. Good metadata supports better understanding and tracking of data assets.
6. Data Access and Security Controls
Data governance ensures that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized users, helping protect privacy and reduce risks of breaches or misuse.
7. Compliance and Risk Management
Governance frameworks help organizations meet regulatory requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO standards by clearly documenting and controlling how data is handled.
Together, these elements form the foundation of strong data governance practices, ensuring that data is not only secure and compliant but also usable and trusted across the business.
Data Governance Benefits
Implementing a strong data governance framework brings long-term value to any organization. From better data quality to improved compliance, the benefits impact both operational efficiency and strategic decision-making.
1. Improved Data Quality
Data governance ensures data is accurate, consistent, and up to date, resulting in more reliable reporting and insights.
2. Regulatory Compliance
With clear data governance policies, businesses can meet legal and industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO with confidence.
3. Stronger Data Security
Data governance sets clear rules about who can view or use specific data. This helps prevent security breaches and keeps sensitive information protected.
4. Better Decision-Making
When data is trusted and well-managed, decision-makers can act faster and with greater confidence, especially in data-driven functions like analytics.
5. Operational Efficiency
Less time is wasted fixing data issues or searching for the right information. This streamlining leads to better productivity across teams.
6. Enhanced Data Value
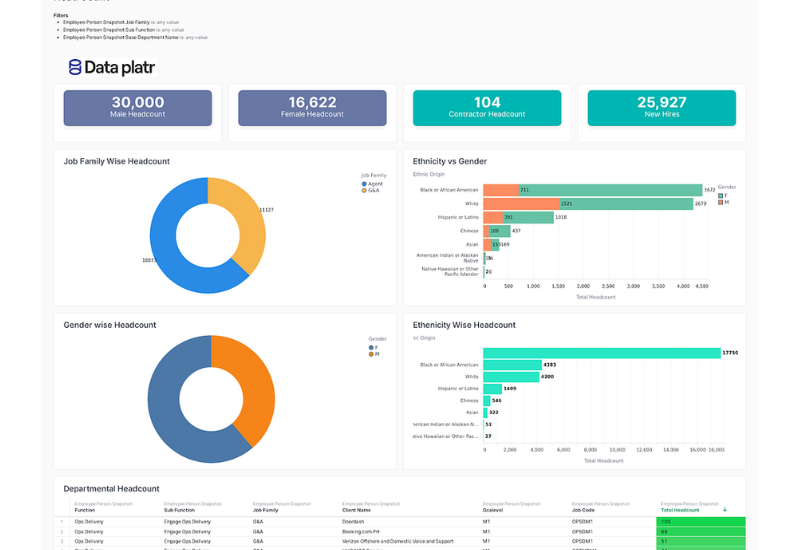
Governed data is more usable and shareable, helping organizations extract more value through clear reporting and data visualization, which simplifies complex information for better insights.
Data governance keeps things safe and drives value. It helps organizations turn raw data into trusted insights, protect sensitive information, and operate more efficiently in a digital world.
Who’s Responsible for Data Governance?
Data governance is a shared responsibility across the organization, but certain roles play key leadership and execution functions to ensure its success.
1. Data Governance Council or Committee
This group sets the overall governance strategy, policies, and priorities. It typically includes executives, department heads, and key stakeholders from IT and business teams.
2. Chief Data Officer (CDO)
The CDO is often the executive sponsor of data governance initiatives. They oversee data strategy and ensure alignment between business goals and data management.
3. Data Stewards
Data stewards are responsible for the day-to-day execution of data governance policies. They monitor data quality, maintain standards, and support business users in managing data properly.
4. IT and Data Management Teams
These teams handle the technical implementation, managing data infrastructure, access controls, security, and integration aligned with governance policies.
5. Business Users and Department Leads
Since they are closest to the data, business users play an important role in defining how data should be used, ensuring it aligns with their operational needs.
Successful enterprise data governance requires collaboration between leadership, IT, and business units. It’s not the job of one person; it’s a company-wide effort to ensure data is trustworthy, secure, and valuable.
Data Governance Implementation
Implementing data governance is not just about compliance. It’s about setting up a sustainable system that ensures your data is accurate, secure, and valuable to every part of the business. Here’s how you can build a strong base, one step at a time.
Step 1: Define Your Objectives and Scope
Start by setting clear goals. Are you aiming to improve data quality, meet compliance standards, or support better analytics? Decide what data domains (like customer, financial, or product data) will be governed first.
Step 2: Assemble Your Governance Team
Form a team that includes a Chief Data Officer (CDO) or sponsor, data stewards, IT leads, and key business users. This group will lead the development and enforcement of governance policies.
Step 3: Create Clear Policies and Standards
Develop a framework of data governance policies that define how data should be accessed, stored, shared, and protected. Make sure responsibilities and escalation paths are documented.
Step 4: Implement the Right Tools
Choose technology platforms that support cloud data governance, metadata management, and data quality monitoring. These tools will help automate enforcement and improve efficiency.
Step 5: Prioritize Data Quality and Metadata
Set up processes for regular data validation and cleansing. Use metadata to track the origin, structure, and purpose of your data assets so users can easily understand and trust the data.
Step 6: Educate and Involve All Stakeholders
Train employees on data governance best practices and how it support their daily work. Awareness is key to adoption, so ensure everyone knows their role in maintaining data integrity.
Step 7: Monitor Progress and Keep Improving
Track metrics such as data accuracy, issue resolution time, and policy compliance. Use these insights to adjust and evolve your data governance strategy over time.
Effective data governance implementation is a continuous process, not a one-time project. With the right team, tools, and commitment, you can build a governance framework that not only protects your data but also drives long-term business success.
Benefits of Data Governance
A well-executed data governance strategy offers significant advantages for businesses of all sizes. It helps organizations manage data more efficiently, reduce risks, and unlock greater value from their data assets.
1. Improved Data Quality
With clear standards and processes in place, data governance ensures data is accurate, consistent, and reliable, leading to better decision-making.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Data governance policies help organizations comply with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and other industry regulations by defining how sensitive data should be handled and protected.
3. Better Decision-Making
Reliable and trusted data supports faster and smarter business decisions, especially in data-driven environments like finance, marketing, and operations.
4. Increased Operational Efficiency
Governed data reduces time spent on fixing errors, searching for information, or resolving data conflicts, resulting in smoother workflows and reduced costs.
5. Enhanced Data Security
By defining access rules and responsibilities, data governance reduces the risk of unauthorized data access and data breaches.
6. Stronger Data Accountability
Clearly defined roles and ownership improve transparency and ensure that everyone knows their responsibility when working with data.
7. Scalable Data Management
As organizations grow, enterprise data governance ensures consistent data practices across departments, systems, and even cloud environments.
Data governance is not just about control; it’s about enabling trust, agility, and long-term value from data. By implementing a strong governance framework, organizations can turn data into a strategic advantage and confidently navigate today’s complex data landscape.
Data Governance Challenges
While data governance offers significant benefits, implementing it successfully is not without its challenges. Many organizations struggle to turn governance frameworks into practical, everyday processes. Here are the typical issues that often come up.
1. Lack of Executive Support
Without leadership support, data governance often lacks the backing, attention, and power it needs to work effectively.
2. Poor Data Culture
If teams see governance as a burden rather than a benefit, adoption will be low. A lack of awareness or data ownership across departments can lead to resistance.
3. Unclear Roles and Responsibilities
Governance fails when no one knows who owns the data, who approves changes, or who enforces standards. Clear role definitions are essential.
4. Inconsistent Data Practices
Different departments may follow their own rules for managing data. Without unified governance, data often ends up disorganized and unreliable.
5. Managing Data Across Systems
In today’s cloud-first and hybrid environments, data often lives in multiple platforms. Cloud data governance requires tools and processes that can scale across complex systems.
6. Resource Constraints
Data governance requires time, tools, and skilled people. Teams often find it hard to manage governance alongside daily work.
7. Measuring Success
It can be difficult to track ROI or demonstrate the value of governance efforts. Without clear KPIs, it’s hard to keep stakeholders engaged long-term.
Implementing data governance takes more than just policies, it requires culture change, collaboration, and continuous effort. By understanding and preparing for these challenges, organizations can build a governance strategy that is both practical and sustainable.
How Does Data Governance Impact Analytics and AI?
As businesses increasingly turn to data for insights, automation, and even generative AI applications, the role of data governance becomes even more critical. High-quality, well-governed data is the foundation of successful analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) initiatives.
Here’s the role data governance plays in analytics and AI success.:
1. Ensures Data Quality for Accurate Insights
AI and analytics can’t perform well without good-quality data. Bad data can give you the wrong answers, but well-managed data keeps things accurate and reliable.
2. Strengthens Data Security and Compliance
AI and analytics often use sensitive or regulated data. Data governance policies ensure that data is used in a compliant and ethical way, reducing risks related to privacy laws and misuse.
3. Promotes Trust in Data-Driven Decisions
When teams know that data is verified and governed, they’re more likely to trust analytics reports and AI recommendations, leading to better, faster decision-making.
4. Enhances Metadata and Data Lineage
Governance provides detailed metadata, which helps analysts and data scientists understand where data comes from and how it's been transformed. This improves model transparency and auditability.
5. Improves AI Model Performance
AI models depend on clean, well-structured data. A solid data governance strategy ensures data consistency, which leads to more accurate predictions and reduced model bias.
Without proper governance, data used in analytics and AI can be incomplete, inconsistent, or even non-compliant. With data governance in place, organizations can unlock the full potential of their analytics and AI efforts, confidently, ethically, and at scale.
Conclusion
Data governance is essential for turning raw data into a trusted and valuable asset. It helps ensure that data is accurate, secure, and used responsibly across the organization.
By enhancing data quality, promoting compliance, and facilitating informed decisions, governance plays a crucial role in driving business success. While it takes effort to implement, the long-term value it brings, especially in analytics and AI, makes it a smart investment.
In simple terms, strong data governance is not just about control. It is about building trust, efficiency, and growth in a data-driven world.